|
|
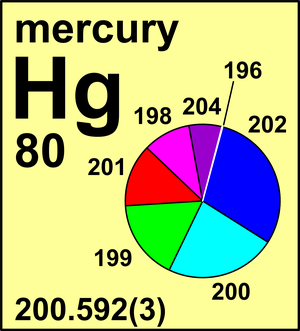
202 Hg Atomic Number
- Symbol: Hg Atomic Number: 80 Atomic Mass: 200.59 amu Melting Point:-38.87 °C (234.28 K, -37.966 °F) Boiling Point: 356.58 °C (629.73 K, 673.844 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 80 Number of Neutrons: 121 Classification: Transition Metal Crystal Structure: Rhombohedral Density @ 293 K: 13.456 g/cm 3 Color: Silver Atomic Structure.
- Atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus): 80; Atomic symbol (on the Periodic Table of Elements): Hg; Atomic weight (average mass of the atom): 200.59.
- Mercury (Hg), chemical element, liquid metal of Group 12 (IIb, or zinc group) of the periodic table. Atomic number 80 atomic weight 200.59 melting point −38.87 °C (−37.97 °F) boiling point 356.9 °C (674 °F) specific gravity 13.5 at 20 °C (68 °F) valence 1, 2 electron configuration 2-8-18-32-18-2.
What Is Hg Atomic Number
How To Find Atomic Number
Good free youtube downloader for mac. Molecular Formula. Mercury, isotope of mass 197. Molecular Weight. Microsoft word for mac torrent 2010.
(Planet Mercury) Known to ancient Chinese and Hindus; found in Egyptian tombs of 1500B.C. Mercury is the only common metal liquid at ordinary temperatures. It only rarelyoccurs free in nature. The chief ore is cinnabar, Spain and Italy produce about 50% of theworld's supply of the metal. The commercial unit for handling mercury is the'flask,' which weighs 76 lb. Gpx to gp5 online converter. The metal is obtained by heating cinnabar in acurrent of air and by condensing the vapor. It is a heavy, silvery-white metal; a ratherpoor conductor of heat, as compared with other metals, and a fair conductor ofelectricity. It easily forms alloys with many metals, such as gold, silver, and tin, whichare called amalgams. Its ease in amalgamating with gold is made use of in the recovery ofgold from its ores. The most important salts are mercury chloride (corrosive sublimate - aviolent poison), mercurous chloride (calomel, occasionally still used in medicine),mercury fulminate, a detonator widely used in explosives, and mercuric sulfide (vermilion,a high-grade paint pigment). Organic mercury compounds are important. It has been foundthat an electrical discharge causes mercury vapor to combine with neon, argon, krypton,and xenon. These products, held together with van der Waals' forces, correspond to HgNe,HgAr, HgKr, and HgXe. Mercury is a virulent poison and is readily absorbed through therespiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, or through unbroken skin. It acts as acumulative poison and dangerous levels are readily attained in air. Air saturated withmercury vapor at 20C contains a concentration that exceeds the toxic limit many times. Thedanger increases at higher temperatures. It is therefore important that mercury be handledwith care. Containers of mercury should be securely covered and spillage should beavoided. If it is necessary to heat mercury or mercury compounds, it should be done in awell-ventilated hood. Methyl mercury is a dangerous pollutant and is now widely found inwater and streams. The triple point of mercury, -38.8344C, is a fixed point on theInternational Temperature Scale (ITS-90).
Sources
Hg Atomic Mass Number
